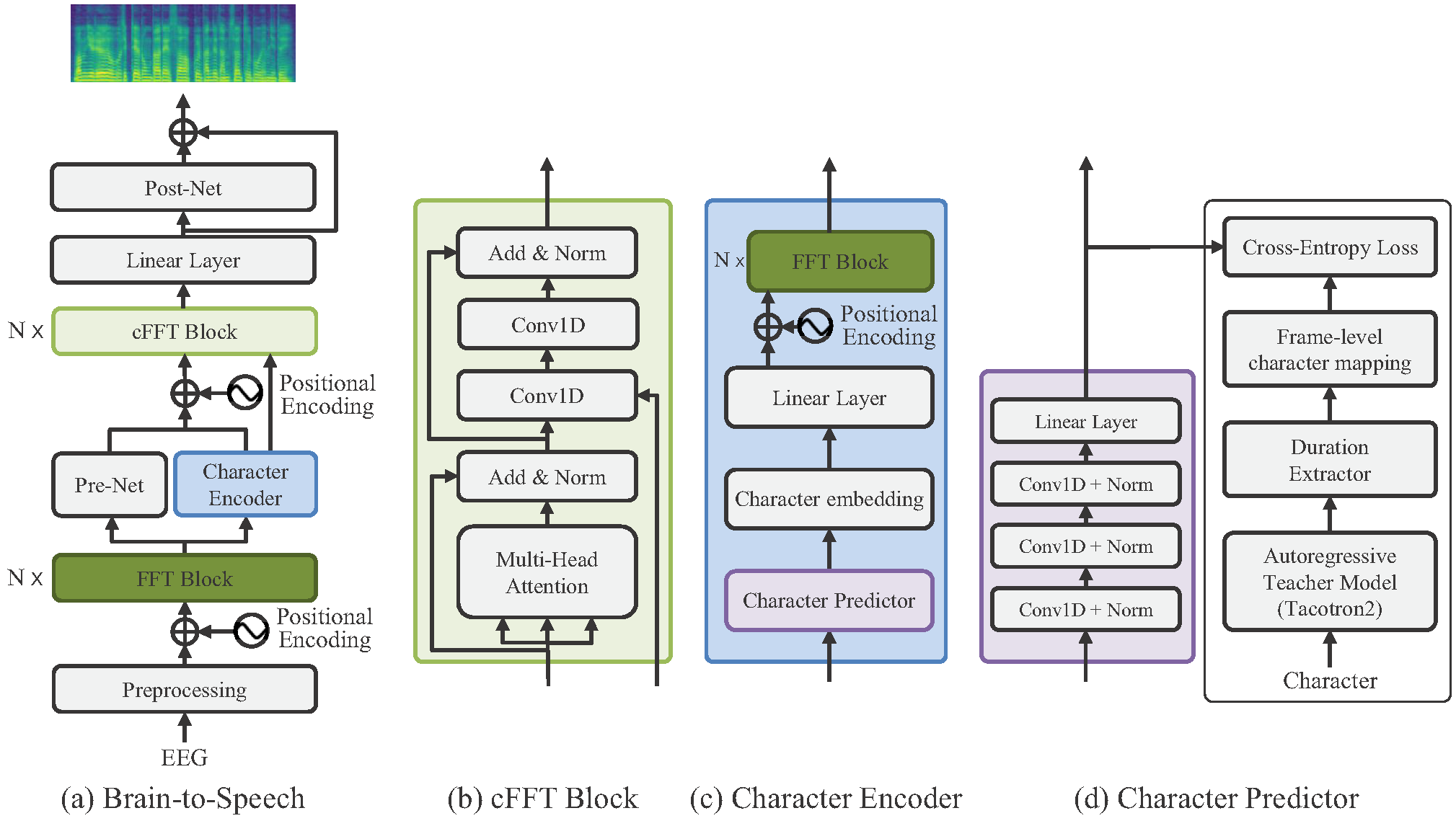
Most communication studies on non-invasive brain signals using a brain–computer interface (BCI) have primarily applied a stimulus-driven approach (e.g., ERP or SSVEP spellers). An invasive brain signal (i.e., Electrocorticography (ECoG)) based speech synthesis was the first technology introduced that translates neural activities into speech from a neural decoding of spoken sentences. The fundamental objective of the present study is to investigate a sentence-level speech synthesis based on non-invasive brain signals, here, Electroencephalography (EEG), for developing more intuitive BCI communication systems. Thus, our study presents a brain-to-speech (BTS) synthesis model that can generate speech from the EEG signals of spoken sentences, namely, a BTS framework. The proposed BTS framework consists of brain signal processing (e.g., recording and artifact removal), frame-level linguistic-conditional feed-forward Transformer networks to generate mel-spectrograms from EEG spectrograms, and a vocoder to generate a high-quality waveform from the neural network generated mel-spectrograms. We extract attention alignments from an encoder-attention-decoder-based autoregressive teacher text-to-speech model for frame-level target character mapping to predict the frame-level linguistic information. In this manner, we successfully demonstrate a non-invasive based sentence-level BTS synthesis for an intuitive BCI communication system. Thus, our study contributes to the deep question of how to solve a sentence-level speech synthesis from a non-invasive brain signal with large noise. The results indicate that the use of the proposed BTS framework could ultimately be beneficial for a brain-to-speech synthesis when developing intuitive BCI communication applications for severely paralyzed patients with neurological disorders or motor disabilities, including those with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or spinal cord injury..
1. Korean : "여기에서 가까운 곳에 서점이 있나요?"
Translation : "Is there a bookstore near here?"
Pronunciation : "yeogieseo gakkaun gos-e seojeom-i issnayo?"
| Raw Audio | Mel + MelGAN |
|---|---|
| Tacotron2(TTS) | FastSpeech(TTS) |
|---|---|
| BTS(with speech-related artifacts) | |
|---|---|
Red color : Wrong Pronanciation |
| BTS(with artifacts removal) | |
|---|---|
Pronunciation : "yeogieseo gakkaun gos-e seojeom-i issnayo?" |
2. Korean : "그는 아주 부지런한 사람이다."
Translation : "He is a very diligent person."
Pronunciation : "geuneun aju bujileonhan salam-ida."
| Raw Audio | Mel + MelGAN |
|---|---|
| Tacotron2(TTS) | FastSpeech(TTS) |
|---|---|
| BTS(with speech-related artifacts) | |
|---|---|
Pronunciation : "geuneun aju bujileonhan salam-ida." |
| BTS(with artifacts removal) | |
|---|---|
Pronunciation : "geuneun aju bujileonhan salam-ida." |
3. Korean : "대규모 구조조정이 불가피합니다."
Translation : "Massive restructuring is inevitable."
Pronunciation : "daegyumo gujojojeong-i bulgapihabnida."
| Raw Audio | Mel + MelGAN |
|---|---|
| Tacotron2(TTS) | FastSpeech(TTS) |
|---|---|
| BTS(with speech-related artifacts) | |
|---|---|
Pronunciation : "daegyumo gujojojeong-i bulgapihabnida." |
| BTS(with artifacts removal) | |
|---|---|
Pronunciation : "daegyumo gujojojeong-i bulgapihabnida." |
4. Korean : "그 둘 중의 하나가 거짓말을 하고 있는 게 분명하다."
Translation : "It is clear that one of the two is lying."
Pronunciation : "geu dul jung-ui hanaga geojismal-eul hago issneun ge bunmyeonghada."
| Raw Audio | Mel + MelGAN |
|---|---|
| Tacotron2(TTS) | FastSpeech(TTS) |
|---|---|
| BTS(with speech-related artifacts) | |
|---|---|
Pronunciation : "geu dul jung-ui hanaga geojismal-eul hago issneun ge bunmyeonghada." |
| BTS(with artifacts removal) | |
|---|---|
Pronunciation : "geu dul jung-ui hanaga geojismal-eul hago issneun ge bunmyeonghada." |
5. Korean : "이 문장은 조금 어색해요."
Translation : "This sentence is a bit awkward."
Pronunciation : "i munjang-eun jogeum eosaeghaeyo."
| Raw Audio | Mel + MelGAN |
|---|---|
| Tacotron2(TTS) | FastSpeech(TTS) |
|---|---|
| BTS(with speech-related artifacts) | |
|---|---|
Pronunciation : "i munjang-eun jogeum eosaeghaeyo." |
| BTS(with artifacts removal) | |
|---|---|
Pronunciation : "i munjang-eun jogeum eosaeghaeyo." |
1. Korean : "범인은 이십대 중반에서 후반의 남성으로 보입니다."
Translation : "The criminal seems to be a man in his mid twenties to late twenties."
Pronunciation : "beom-in-eun isibdae jungban-eseo huban-ui namseong-eulo boibnida."
| Spoken Speech (Raw audio) |
Mimed Speech (Raw audio) |
|---|---|
| Spoken Speech (BTS with artifacts removal) |
|
|---|---|
Pronunciation : "beom-in-eun isibdae jungban-eseo huban-ui namseong-eulo boibnida." |
| Mimed Speech (BTS with artifacts removal) |
|
|---|---|
Pronunciation : "beom-in-eun i sibdae jung ban-eseo huban-ui namseong-eulo boibnida." |

Code for training and inference will be released after the paper is accepted
EEG and audio data used to create Figure 3 and 4 will be available from the public repository when the paper is accepted. Additional materials can be requested from author upon reasonable request.